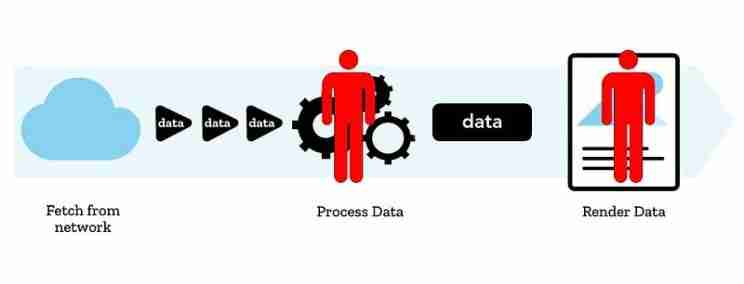
我们首先解释一下数据是如何通过网络发送的。它不是作为单个连续流发送的;相反,它被分成更小的块。在接收端,消费者或应用程序负责在收到所有数据后以正确的顺序和格式重新组装这些块。对于图像、视频和其他相对较大的数据类型,此过程会自动发生。
因此 streams api 提供的是一种无需等待完整数据可用的方法
修订文本:“streams api 提供的是一种在数据到达时处理数据的方法,而不是等待整个数据集可用。以下是两个主要优点:
让我们首先比较使用 fetch api 接收数据的传统方法与新的 streams api 方法。
fetch("url") .then((response) => {
// note that there is a middle step before we receive the final data
// let's see what we actually receive
console.log(response.body); return response.text(); }) .then((data) => { // perform operations with the data
});
在此示例中,response.body 是一个 readablestream 对象:
readablestream { locked: false, state: 'readable', supportsbyob: true }
在这里,我们遇到了 streams api 的第一个组件:readablestream。 readablestream 构造函数创建并返回一个可读的流对象,这使我们能够更有效地处理流数据。我们可以使用这个构造函数来管理数据块,而不是等待整个数据集可用。
{ arraybuffer(): promise<arraybuffer>; blob(): promise<blob>; formdata(): promise<formdata>; json(): promise<any>; text(): promise<string>; }
</string></any></formdata></blob></arraybuffer>
我们需要实现一个函数来处理对象以访问实时发送的数据。这个函数应该:
1 接收 readablestream 作为承诺。
深入 readablestream
interface readablestream<r any> {
readonly locked: boolean;
cancel(reason?: any): promise<void>;
getreader(options: { mode: "byob" }): readablestreambyobreader;
getreader(): readablestreamdefaultreader<r>;
getreader(options?: readablestreamgetreaderoptions): readablestreamreader<r>;
pipethrough<t>(
transform: readablewritablepair<t r>,
options?: streampipeoptions
): readablestream<t>;
pipeto(
destination: writablestream<r>,
options?: streampipeoptions
): promise<void>;
tee(): [readablestream<r>, readablestream<r>];
}
</r></r></void></r></t></t></t></r></r></void></r>
interface readablestreamdefaultreader<r any>
extends readablestreamgenericreader {
read(): promise<readablestreamreadresult>>;
releaselock(): void;
}
</readablestreamreadresult></r>
为了使用流,我们使用 getreader() ,它返回一个 readablestreamdefaultreader。
下面是一个示例,我们向 lichess.org 的 api 向某个用户请求 pgn 格式(将其视为文本)的游戏。最终结果应该以文本形式呈现。
fetch("https://lichess.org/api/games/user/gg").then((response) => {
console.log(response);
const readablestream = response.body;
console.log(readablestream);
const reader = readablestream.getreader();
console.log(reader);
});
输出:
readablestream { locked: false, state: 'readable', supportsbyob: true } readablestreamdefaultreader { stream: readablestream { locked: true, state: 'readable', supportsbyob: true }, readrequests: 0, close: promise { <pending> } }
</pending>
请注意,您不能同时拥有多个读取器,因为如果 readablestream.locked = true,getreader() 将抛出错误,因此如果您想更改读取器,您必须首先使用 readablestreamdefaultreader 释放锁定。释放锁()
fetch("https://lichess.org/api/games/user/gg").then((response) => {
const readablestream = response.body;
console.log(readablestream);
const reader = readablestream.getreader();
console.log(reader);
try {
reader.releaselock();
const reader2 = readablestream.getreader();
// won't throw an error
const reader3 = readablestream.getreader();
// will throw an error
} catch (e) {
console.error(e.message);
// invalid state: readablestream is locked
}
});
现在我们在阅读器中使用 read 函数,它有两个变量
let string = result.push(
value.reduce((p, c) => {
return p + c.fromcharcode();
}, "")
); // or
let string = new textdecoder().decode(value);
// both achieve the same thing converting uint8array to string
完整代码示例
fetch("https://lichess.org/api/games/user/gg")
.then((response) => {
return new promise((resolve, reject) => {
const readablestream = response.body;
const reader = readablestream.getreader();
let result = [];
reader.read().then(function handlechunks({ done, value }) {
if (done) {
resolve(result);
return;
}
const pgn = new textdecoder().decode(value);
result.push(pgn);
reader.read().then(handlechunks);
});
});
})
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
});
// console.log(value)
uint8array(551) [
91, 69, 118, 101, 110, 116, 32, 34, 82, 97, 116, 101,
100, 32, 98, 108, 105, 116, 122, 32, 103, 97, 109, 101,
34, 93, 10, 91, 83, 105, 116, 101, 32, 34, 104, 116,
116, 112, 115, 58, 47, 47, 108, 105, 99, 104, 101, 115,
115, 46, 111, 114, 103, 47, 90, 122, 78, 66, 90, 119,
100, 71, 34, 93, 10, 91, 68, 97, 116, 101, 32, 34,
50, 48, 50, 48, 46, 48, 49, 46, 49, 48, 34, 93,
10, 91, 87, 104, 105, 116, 101, 32, 34, 86, 101, 101,
118, 101, 101, 50,
... 451 more items
]
// console.log(new textdecoder().decode(value))
[event "rated blitz game"]
[site "https://lichess.org/zznbzwdg"]
[date "2020.01.10"]
[white "veevee222"]
[black "gg"]
[result "0-1"]
[utcdate "2020.01.10"]
[utctime "20:21:02"]
[whiteelo "1858"]
[blackelo "1863"]
[whiteratingdiff "-6"]
[blackratingdiff "+35"]
[variant "standard"]
[timecontrol "180+0"]
[eco "c00"]
[termination "normal"]
1. e4 e6 2. d4 d6 3. c4 Nf6 4. Nc3 c5 5. f4 cxd4 6. Qxd4 Nc6 7. Qd1 b6 8. g3 Bb7 9. Bg2 Rc8 10. Nf3 Be7 11. O-O O-O 12. b3 Nb4 13. Bb2 a5 14. Re1 Qc7 15. a3 Na6 16. Rc1 Nc5 17. Qd4 Nxb3 18. Qd1 Nxc1 19. e5 0-1
例如链接
例如,完整代码请
现在,我们可以在游戏通过网络发送的 pgn 时逐步访问它们。例如,如果我们在网站 ui 中使用已加载的游戏,则用户无需在空白或加载屏幕前等待,直到所有游戏都加载完毕。相反,数据可以逐步显示,从用户体验的角度来看,这要好得多。
例如完整代码请移至此处